
Unveiling the Dual Impact of Race and Gender on Athletes’ Earnings
By Darius Spearman (africanelements)
Support African Elements at patreon.com/africanelements and hear recent news in a single playlist. Additionally, you can gain early access to ad-free video content.
| Key Takeaways |
|---|
| Racial and gender disparities in sports salaries significantly impact athletes, with women of color facing the most severe pay gaps. |
| Legislative measures like Title IX have made strides towards equality, but gaps remain, particularly in professional sports. |
| Media coverage heavily influences salary disparities, favoring male-dominated sports and exacerbating the pay gap. |
| Advocacy and policy reform are crucial for achieving equity, with a need for fans and stakeholders to actively push for change. |
| Engaging with and supporting women’s sports can drive attention and resources towards shrinking the gender pay gap in sports. |
Bridging the Gap: Addressing Racial and Gender Disparities in Sports Salaries
Exploring the persistent salary inequalities in professional sports reveals complex, systemic issues. Notably, female athletes, especially those of color, continue to fight for equal pay. They face significant challenges in a space historically dominated by male counterparts. This article will delve into the roles of media exposure and legislative measures in shaping these disparities. Additionally, it emphasizes how advocacy and proactive policies are essential for change.
Firstly, significant strides toward gender and racial equity in sports have been made, yet the playing field remains uneven. For instance, Title IX has increased opportunities for women in sports, but professional arenas still reflect substantial pay discrepancies (Title IX, 2020). Furthermore, media coverage amplifies these gaps. Men’s sports typically draw more viewership, leading to higher revenues and, subsequently, higher salaries. Also, policy interventions and public support are crucial for advancing equity. They highlight the need for a concerted effort to alter the status quo.
This article examines the intertwined issues of race and gender in sports salaries to bridge these disparities. It emphasizes the need for comprehensive reforms and community engagement to support female athletes. Together, we can foster a more inclusive and equitable sports industry.
Historical Overview of Pay Inequality in Sports
The Roots of Racial and Gender Salary Gaps
The foundations of professional sports were built on segregation by both race and gender, establishing disparities that resonate today. Indeed, these early decisions created systemic barriers that continue to affect salary norms. Clearly, the historical context is critical for understanding the current disparities in sports salaries.
Impact of Legislation on Sports Equity
Title IX and subsequent diversity initiatives have transformed the landscape. Still, the benefits have not been uniformly distributed across all groups. Moreover, these changes have sparked significant, albeit uneven, progress in equity in sports. Thus, while progress is evident, substantial gaps persist.
“Despite advancements like Title IX aimed at leveling the playing field in sports, racial and gender disparities persist, with Black women earning significantly less than their white counterparts across professional leagues.” (DukeSpace)
What is Title IX?
Title IX is a comprehensive federal civil rights law that prohibits discrimination on the basis of sex. It applies to any education program or activity that receives federal financial assistance.
Key Points about Title IX
- Title IX states: “No person in the United States shall, on the basis of sex, be excluded from participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination under any education program or activity receiving Federal financial assistance.”
- It applies to all educational institutions that receive federal funding, including elementary and secondary schools, colleges, universities, and other educational entities.
- Title IX prohibits sex-based discrimination in all areas of education, including admissions, recruitment, financial aid, academic programs, athletics, housing, employment, and sexual harassment/violence.
- Furthermore, sexual harassment and sexual violence (including sexual assault, dating violence, domestic violence, and stalking) are forms of sex discrimination prohibited by Title IX.
- Importantly, educational institutions must have procedures in place to prevent, investigate, and resolve complaints of sex discrimination, including designating a Title IX coordinator.
- Title IX requires schools to take prompt and effective action to address sexual harassment/violence, prevent its recurrence, and remedy its effects.
- Retaliation against individuals for making Title IX complaints or participating in investigations is prohibited.
- Lastly, Recent interpretations have clarified that Title IX’s prohibition on sex discrimination includes discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity.
In summary, Title IX is a landmark civil rights law. It aims to ensure equal access to education free from sex-based discrimination in federally funded educational programs and activities.
Examining Disparities in High-Profile Sports Leagues
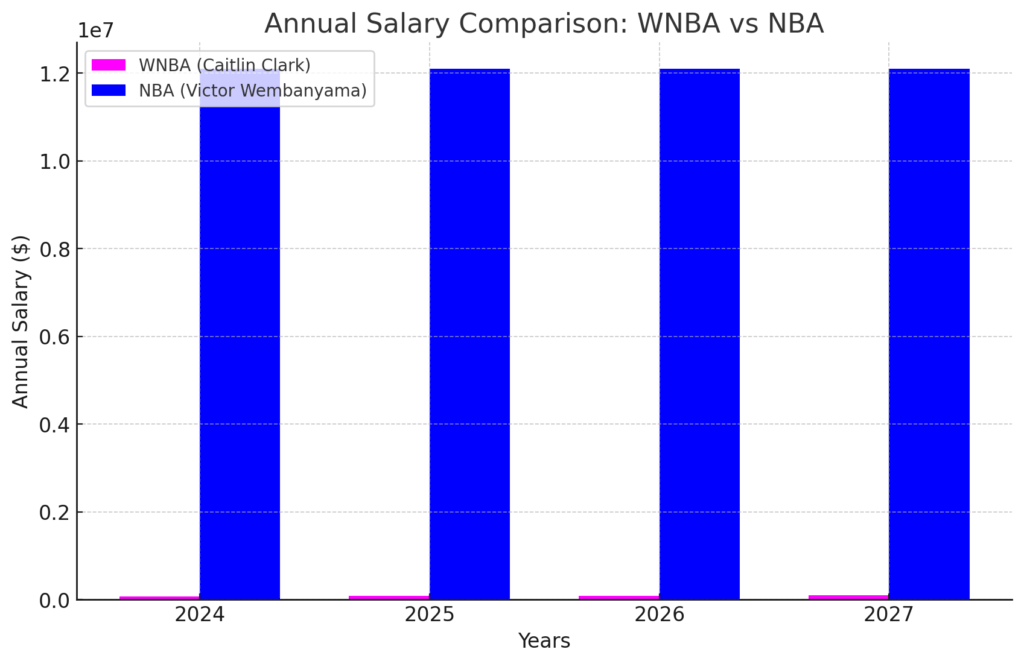
Analyzing the Broader Implications of WNBA Salary Gaps
In the WNBA, salary disparities sharply reflect broader societal inequalities, particularly impacting athletes of color. Furthermore, these financial structures compel many athletes to seek opportunities overseas, highlighting the global impacts of domestic pay gaps. Clearly, the WNBA’s salary issues underscore systemic challenges within sports leagues.
“Cherelle Griner highlighted that despite Brittney Griner‘s star status and championship wins, she had to play overseas due to inadequate WNBA compensation.” (NewsOne)
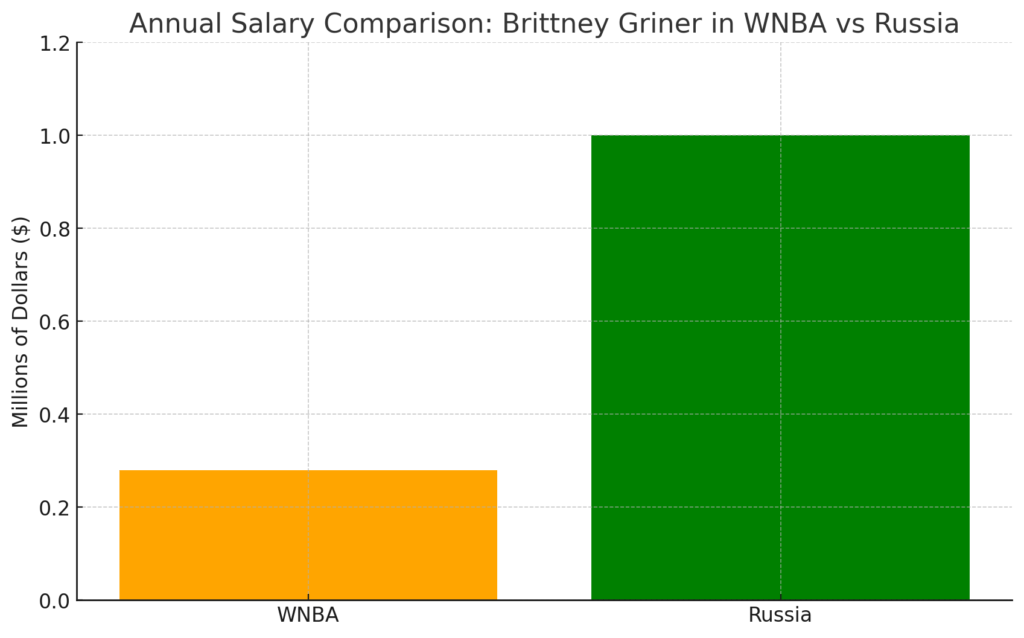
Racial Disparities within the Gender Pay Gap
The gender pay gap disproportionately impacts women of color. Notably, Black women in the U.S. earn just 63 cents for every dollar earned by white men. Conversely, white women earn 79 cents on the dollar. This disparity indicates a deeper issue beyond gender, highlighting racial inequalities within the pay structure.
Moreover, in professional sports like basketball and soccer, the composition of athletes varies significantly between women’s and men’s leagues. Women’s leagues have a higher proportion of white athletes, whereas men’s leagues are more diverse, featuring a higher number of Black athletes. This composition significantly affects pay disparities along racial lines. Consequently, white female athletes often face different economic conditions compared to their Black counterparts and other minority groups in the same sports. Consequently, Black, Latina, and other minority female athletes experience compounded pay inequities (DarrasLaw; Columbia Law Review).
Lack of Opportunities and Representation
Socioeconomic factors and limited access to sports like tennis, golf, and swimming. As a result, this lack of access creates barriers for girls of color from a young age. These barriers prevent many from participating in and advancing within these sports, which are traditionally seen as “white” sports (New York Times).
Additionally, women of color are underrepresented in leadership and coaching roles in both professional and collegiate sports. This lack of representation limits the availability of role models and mentors for young athletes of color, further perpetuating the cycle of limited opportunities. Importantly, the focus on gender equity through Title IX has primarily benefited white women, often overlooking the intersectional challenges Black female athletes and other women of color face (University of Michigan).
Stereotypes and Discrimination
Stereotypes and discrimination based on race, gender, and sexuality significantly influence public interest, media coverage, sponsorship opportunities, and endorsement deals for female athletes of color. These biases affect their marketability and, consequently, their earning potential beyond just competition prize money.
Particularly, female athletes who challenge stereotypical notions of femininity, especially Black women and LGBTQ+ women, may face more backlash and reduced marketability. This scenario underscores the pervasive influence of racist and sexist ideologies on the perceived value and revenue-generating capacity of women’s sports. These ideologies often justify the lower salaries and investment in women’s sports compared to men’s (DarrasLaw; Columbia Law Review).
In summary, the gender pay gap in professional sports is exacerbated by racial disparities, with women of color facing compounded disparities due to intersecting forms of discrimination, lack of opportunities and representation, as well as stereotypes that impact their marketability and earning potential. Addressing this complex issue requires a multifaceted approach considering the unique challenges diverse female athletes face (DarrasLaw; University of Michigan; Columbia Law Review; New York Times).
The Societal Impact of Salary Disparities in Sports
Media and Sponsorship Biases
Media representation and sponsorship opportunities are often skewed by racial and gender biases. Such biases significantly affect the commercial success of leagues like the WNBA. Furthermore, these biases hinder equal financial opportunities for women of color in sports, perpetuating the cycle of inequity.
Consequences of Media and Sponsorship Disparities
The lack of media attention and unequal sponsorship deals further widen the pay gaps between male and female athletes. Moreover, these factors play a crucial role in perpetuating the economic disparities observed in professional sports today, impacting athletes’ careers and lives beyond the field.
“Despite high performance and significant achievements, women in sports like the WNBA suffer from lower sponsorship and media attention compared to men’s leagues, impacting their overall earnings and professional growth.” (NBC News)
Advocacy and Policy Directions for Future Equity
The Role of Advocacy in Sports
Advocacy plays a critical role in pushing for equitable pay in sports. Moreover, intersectional advocacy is essential for addressing the nuanced disparities that affect female athletes of color.
Policy Interventions for Gender and Racial Equity in Sports
Proposing policy changes can offer targeted solutions to the ingrained inequities in sports salaries. These interventions could also significantly benefit all athletes, particularly those from marginalized groups, ensuring a fairer sports industry overall.
“Calls for policy interventions in sports, such as equal pay mandates and increased transparency in salary negotiations, could help address these deep-seated inequities.” (DukeSpace)
FAQs
Q: Why do female athletes often earn less than male athletes?
A: Female athletes often earn less due to longstanding gender biases in sports, lower media coverage, and smaller revenues in women’s sports leagues.
Q: How does racial disparity affect salary in sports?
A: Racial disparities compound gender pay gaps, especially affecting women of color who may face more significant barriers and biases in sports.
Q: What role does media play in sports salary disparities?
A: Media plays a crucial role by influencing public interest and sponsorship dollars. Higher coverage of male sports leads to greater revenues and hence higher salaries.
Q: Can policy changes improve pay equity in sports?
A: Yes, policy interventions like equal pay legislation and transparency in sports financing can help address pay disparities in sports.
Q: How can fans support gender and racial equity in sports?
A: Fans can support equity by attending women’s sports events, advocating for media coverage of female sports, and supporting brands that endorse female athletes.
About the author
Darius Spearman is a professor of Black Studies at San Diego City College. There, he has been pursuing his love of teaching since 2007. He is the author of several books, including Between The Color Lines: A History of African Americans on the California Frontier Through 1890. You can visit Darius online at africanelements.org.
